China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News. This article dives into China’s incredible manufacturing dominance, exploring its historical rise, key sectors, global impact, and future challenges. We’ll examine how China became a global manufacturing hub, its role in international supply chains, and the implications for the world economy. Get ready for a fascinating look at the powerhouse that shapes global production.
So, the Hacker News thread on China’s manufacturing dominance is fascinating, right? It got me thinking about global power dynamics – how a nation’s industrial might impacts everything. Then I saw this amazing sports news story: Real Madrid Secures Victory With Ten Men Against Valencia , which shows how even with setbacks, a strong team can still triumph.
It reminds me of how China’s manufacturing prowess, despite global challenges, continues to be a major force.
We’ll cover everything from the historical context and key policy decisions that fueled China’s manufacturing boom to the current challenges it faces, such as rising labor costs and environmental concerns. We’ll also compare China’s manufacturing prowess to other leading nations and explore the future trends shaping this dynamic sector. Think automation, AI, and the ongoing shift in global supply chains.
China’s Manufacturing Powerhouse: China Is The Manufacturing Superpower | Hacker News
China’s ascent to global manufacturing dominance is a remarkable story of economic transformation. From a largely agrarian society, it has become the world’s factory, shaping global trade and impacting countless industries. This article explores the key factors driving China’s manufacturing success, its current challenges, and its future prospects.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance: A Historical Perspective
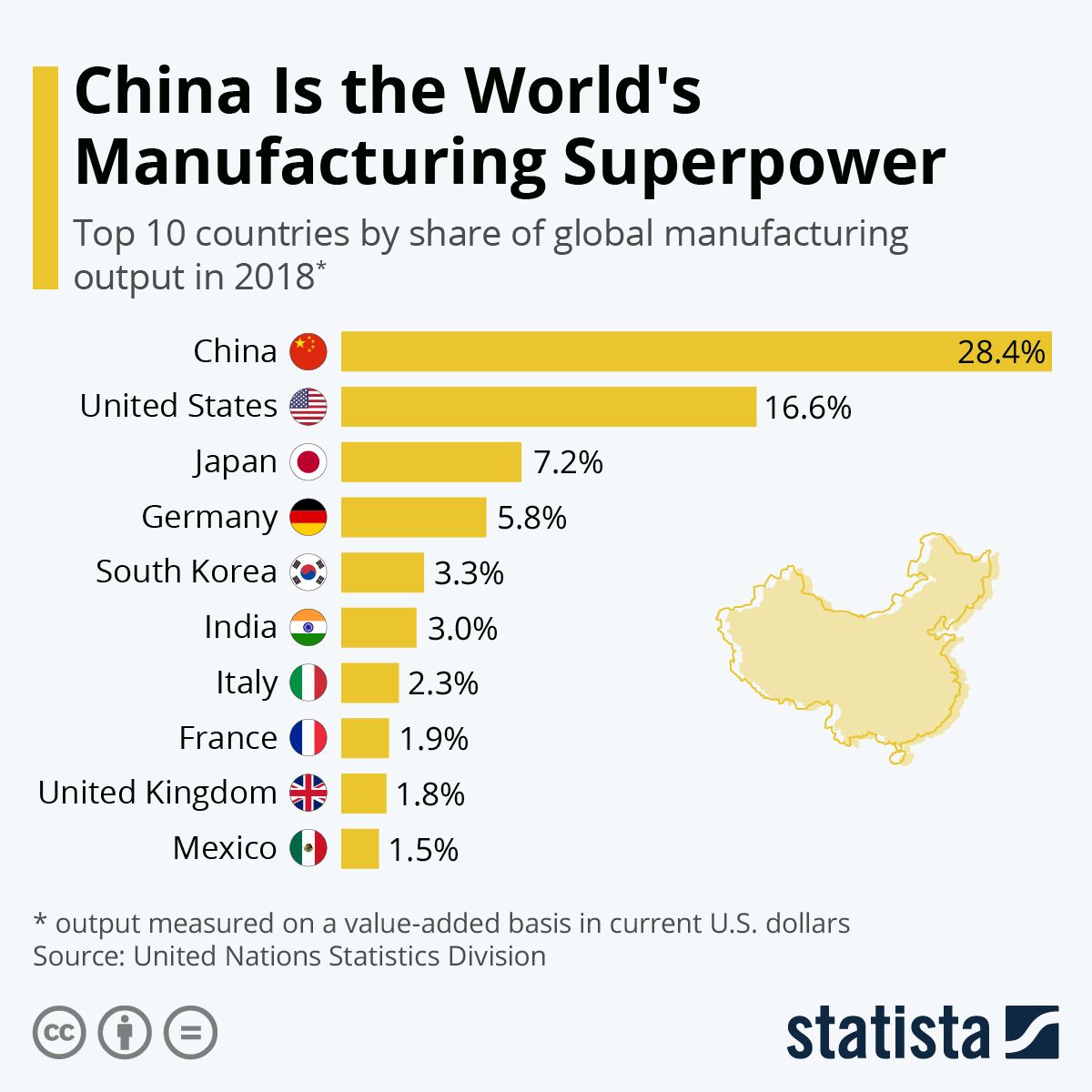
China’s manufacturing evolution is a multi-decade journey marked by strategic policy shifts and remarkable economic growth. Its trajectory differs significantly from other manufacturing giants, demonstrating a unique blend of government planning and market-driven expansion. This section details key milestones and contributing factors.
| Date | Event | Impact | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1978 | Economic Reforms under Deng Xiaoping | Opened China to foreign investment and initiated market-oriented reforms, laying the foundation for rapid industrial growth. | Deng Xiaoping’s speeches and policy documents outlining the reforms. |
| 1980s-1990s | Special Economic Zones (SEZs) established | Attracted foreign direct investment (FDI) and spurred export-oriented manufacturing. | Data on FDI inflows into SEZs and export growth during this period. |
| 2001 | Accession to the World Trade Organization (WTO) | Granted China greater access to global markets and further accelerated its manufacturing expansion. | WTO accession agreement and subsequent trade data. |
| 2010s-Present | Focus on technological advancement and domestic consumption | Shift towards higher value-added manufacturing and reduced reliance on low-cost exports. | Government reports on industrial policy and economic data on domestic consumption. |
Key Sectors of Chinese Manufacturing

China’s manufacturing prowess is spread across diverse sectors, each contributing significantly to its global influence. This section highlights dominant sectors, their technological capabilities, and key players.
| Sector | Output Share (Illustrative) | Technological Capabilities | Key Companies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics | 30% | High-volume production, advanced assembly, increasing R&D in semiconductors. | Huawei, Xiaomi, Foxconn |
| Textiles | 15% | Automation in textile production, advanced materials, focus on sustainable practices. | Shenzhou International, Shandong Ruyi |
| Automotive | 10% | Electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing, autonomous driving technology, increasing domestic brands. | BYD, SAIC Motor, Geely |
| Other (machinery, steel, etc.) | 45% | Wide range of capabilities, from basic to advanced machinery production. | Various state-owned enterprises and private companies |
Global Supply Chains and China’s Role, China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News

China’s integration into global supply chains is undeniable. Its role as a manufacturing hub has both advantages and disadvantages for companies worldwide. This section analyzes China’s central position and the geopolitical factors impacting it.
For example, a hypothetical scenario of a significant disruption to China’s manufacturing capabilities, perhaps due to a major natural disaster or prolonged geopolitical instability, could lead to global shortages of various goods, impacting industries worldwide and causing significant economic disruption. The interconnectedness of global supply chains highlights China’s critical role.
Challenges and Future Trends in Chinese Manufacturing
Despite its dominance, China’s manufacturing sector faces evolving challenges. This section explores these challenges, China’s strategic responses, and predictions for the future.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – a lot of those products probably use AI-powered systems in their creation. For example, creating engaging e-learning content is easier now than ever, thanks to advancements in AI voice generation. Check out this guide on how to choose the best AI voice generator for e-learning to see how this tech impacts even seemingly unrelated fields.
Ultimately, China’s manufacturing prowess is intertwined with global technological advancements, making it a fascinating area of study.
- Rising labor costs: China is shifting towards automation and higher-value manufacturing to offset rising wages.
- Environmental concerns: Stringent environmental regulations are pushing for cleaner and more sustainable manufacturing practices.
- Technological competition: China is investing heavily in R&D to maintain its technological edge and compete with other manufacturing powerhouses.
- Trade tensions: Geopolitical factors continue to influence China’s position in global supply chains.
Predictions for the future of Chinese manufacturing include a continued focus on technological innovation, a shift towards higher value-added manufacturing, and increasing integration into global value chains, albeit with a more balanced and diversified approach.
Comparative Analysis: China vs. Other Manufacturing Powerhouses
Comparing China’s manufacturing capabilities with other leading nations reveals both strengths and areas for improvement. This section provides a comparative overview, highlighting key metrics and competitive landscapes.
A visual representation comparing key metrics (e.g., manufacturing output, R&D spending, labor costs, automation levels) across China, the US, Germany, and Japan would reveal China’s strengths in scale and cost-effectiveness, while highlighting the competitive advantages of other nations in specific technological areas and high-value manufacturing.
The Impact of Chinese Manufacturing on Global Trade
China’s manufacturing sector has profoundly reshaped global trade patterns and economic relationships. This section examines its impact on global trade balances, price levels, employment, and overall economic stability.
For instance, the availability of low-cost goods from China has influenced consumer spending globally, impacting price levels and consumer purchasing power. Simultaneously, the shift of manufacturing to China has impacted employment levels in other countries, leading to both job losses and the creation of new opportunities in different sectors.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance is interesting, especially considering global supply chains. It makes you think about product safety, like this recent recall: Sea and Himalayan salts recalled in Canada: ‘Do not use, serve or’. The incident highlights the need for robust quality control, no matter where the product originates, even if it’s from a manufacturing powerhouse like China.
Closure

China’s manufacturing dominance is undeniable, but its future trajectory is far from certain. While it faces significant hurdles, its adaptability and continued investment in technology suggest a lasting influence on the global economy. Understanding China’s manufacturing sector is crucial for anyone involved in global trade, supply chain management, or economic forecasting. The journey from a largely agrarian society to the world’s factory is a compelling story of economic transformation, and one that continues to unfold daily.
FAQ Resource
What are some examples of successful Chinese manufacturing companies?
Huawei, Tencent, Alibaba (though not purely manufacturing, they heavily rely on and influence manufacturing), and numerous others in electronics, textiles, and automotive sectors.
How does China’s manufacturing impact the environment?
It has led to significant pollution challenges, but China is increasingly investing in greener manufacturing practices and renewable energy sources to mitigate these effects.
What are the risks of relying solely on Chinese manufacturing?
Geopolitical instability, trade wars, supply chain disruptions, and human rights concerns are key risks.
Is China’s manufacturing dominance likely to continue indefinitely?
It’s unlikely to remain completely unchallenged. Other countries are investing in their own manufacturing capabilities, and automation could shift the balance.
